What I know is that online piracy is flourishing. What I know is that the internet has become a topsy-turvy world where criminals are celebrated as heroes, and their victims demonized. What I know is that I’m tired—tired of listening to the red herrings and hyperbole ricocheting around the web in opposition to (overdue) legislative efforts to do something about it. Here’s what I know…
First of all, make no mistake, the vast majority of today’s piracy is driven by the thing that has motivated mankind since time began—the desire to make money. If you take the time to spend a few minutes online exploring websites engaged in piracy (most people who speak out on the issue don’t seem to bother) you’ll quickly recognize that money is at the center of everything.

Mediafire download link (for flm-Unhappy Birthday) featuring Google ads.
If the ads aren’t hitting you squarely in the face, or the offers of high-speed, high quality downloads don’t spark suspicion, then perhaps it’s time to clean your glasses. How ‘bout I take you on a tour?
Let’s begin with the sites that serve as the lynchpin for today’s online pirates. No, I’m not going to talk about Pirate Bay or other notorious P2P (peer to peer) sites. No need for that. Consumers are all about convenience, and it’s not particularly convenient to download torrents and reconfigure the numerous file parts in order to view a movie. Today it’s all about the one-stop shopping experience, and for that there’s no better storefront than the cyberlockers where, with the click of a mouse, you can download (or watch) your favorite film. You’ll likely find other items on your wish list (e-books, music, software, and more) available for easy download as well.
You’ve probably heard the term “cloud based storage” floating around a lot lately. Well, thanks to companies like Apple, and the recent launch of their cloud based offering called “iCloud,” the notion of storing files online via a virtual hard drive is gaining ground. Cyberlockers have been providing this “service” for nearly half a decade now, and while there is legitimate activity taking place via some cloud-based storage sites like Drop Box and Yousendit, there are many others whose business model is predicated on content theft. The now disabled Megaupload.com is a good example of the latter variety. (Read the indictment for a step-by-step tour through the inner-workings of their criminal enterprise.)
How does an illicit Megaupload-like business model work? Well, if you want to understand how cyber lockers work it’s helpful to think of a company like Amway. Amway’s business success popularized the multi-level marketing style pyramid business model (or scheme ) whereby the operators at the top of the pyramid recruit people to work for them. They, in turn, recruit more workers who, in turn, sell products to the public. Those at the top make money only if they can recruit, and keep, enough people below to do the actual work. Those doing the bulk of the work earn money, but at a much lower rate than those at the top. It’s the trickle up theory of profits.
At any rate, if you journey to the cyberlocker of your choice–Megaupload, Filesonic, Fileserve, Filefactory, Uploading, Uploadstation, Mediafire, Megashares, Sockpuppet, Putlocker, etc. you will see enticements offered encouraging visitors to join this type of profit pyramid.

Cyber lockers offer CASH for uploads.
Why do they do this? Well the cyberlocker business model depends on traffic. In order to drive traffic to their site they need content that will attract visitors. What better carrot than popular movies, books or music? Never mind copyright, there’s the “safe harbor” provision of the DMCA that allows the cyberlocker operators to essentially look the other way (plead ignorance) when it comes to the content that affiliates upload. In fact, if uploaders did abide by a site’s published Terms of Service, the cyberlockers would quickly be out of business.

In other words, cyberlockers depend on an army of affiliates to do the dirty work for them. It’s a scenario that enables the cyberlockers to shield themselves from legal liability, while their servers are simultaneously receiving thousands of (stolen) files every day–fresh content sure to attract new (and returning) customers.
So, in order to set this eco-system into motion, the cyberlockers lure their minions. Uploaders can earn rewards, which usually start at around $35 per 1,000 downloads. Simply put, the more downloads you generate for your file, the more money you earn.

Cyberlockers are booming thanks to profits from piracy.
That fact sets in motion the next level of piracy—the viral spread of the download links. The affiliate armies take their links and post them on download (Warez) forums far and wide. The more these links are “shared” across the web, the more money made.

Click to for PDF with 36 posts of viral links.
To further ensure their earnings, these cyberlocker affiliate pirates—I’ll refer to them as CAPs from now on–usually upload their stolen files to multiple cyberlocker sites. This is called ‘mirroring” and what it means is that if a link is disabled on one cyberlocker site you can easily find the identical file on another. Each CAP generally has affiliate accounts with multiple cyberlockers so that their illicit income won’t suffer if some links are disabled.
Since they are paid per download to maximize profits, CAPs often break a film file into several parts. An average size for an uploaded film is around 700 MB (HD films can easily be double that size) but if divided into smaller chunks, requiring multiple links, and thus multiple downloads, the CAP can earn more download points. There’s a trade-off to this approach, however, as it can dissuade downloaders who prefer the convenience factor of downloading a “single” file.

Film download broken into several links in order to maximize profits.
Some sites like Megavideo (the streaming partner site to Megaupload) offer visitors the ability to watch an entire film streaming online with no download wait time. Watch the film, and if you like it, you can add it to your “collection” and download a copy for later viewing.
So, now that it’s pretty easy to understand how so much illegal content gets uploaded to the cyberlocker sites, let’s look for a moment how site operators turn that traffic into actual income.
At the top of the list is online advertising. Click a cyberlocker download link and you will arrive at a page like this.

Cyber locker site streaming the film “Unhappy Birthday” with Netflix ads serviced by Google.
There’s a link or stream for a film and there are ads. Various companies serve these ads, but one can’t ignore the fact that Google and other U.S. based ad servers like AdBrite are ubiquitous on the cyberlockers. For the record, the ads seen on the image above and below are served by Google, though now that they’ve changed their icon and obscured their connection to them, it’s more difficult to tell. In any case, no matter who serves the ad, the cyberlocker makes money and the ad service provider makes money. The creator gets squat.

Another cyber locker stream with more ads (provided by Google).
In addition to ad income, cyberlockers derive profit by offering “subscriptions.” In this instance users pay a fee, averaging around $9.00 per month, that enables high-speed downloads on the website. This means instead of waiting a half hour to download a full film, the entire process takes only 3 minutes. For those who are repeat customers, this may be money well spent. In this instance the cyberlocker site is making money and the payment processors (Visa, MasterCard, PayPal and the like) are making money. Again, the content creator earns ZERO.

Cyber lockers cash in on selling subscriptions for high speed downloads.
In order to boost its subscriptions cyber lockers again turn to affiliate rewards. Remember those forums where the CAPs go to spread their viral seed? Well, many, if not most of those forum operators also have relationships with the cyberlockers and are an integral part of the piracy profit pyramid. For every individual they “refer” who becomes a cyberlocker affiliate, they earn a referral fee. Thanks to unfettered access to free content and income, the eco-system of online piracy continues to thrive and grow.

HD-BB an online forum where viral cyberlocker links are spread.

Click image for PDF of some forum threads.
HD-BB is just one example of such a forum. The forum operators boast of the high-quality “rips” shared by its members. If you drill down into forum posts you’ll quickly discover that moderators only allow users to post links to specific, “approved” cyberlockers that the forum has a relationship with. There are also links that direct users to the various affiliate options ensuring that the forum earns its fair share. The forum makes money, the cyberlocker makes money and the creator of the content makes ZERO.
This is what I know.
Now that this black market business model is entrenched as a way of doing business around the globe, what can be done to stop it? Well, I’m afraid that nothing can stop it–piracy will never disappear entirely–but something can be done to mitigate its effects. This can happen if we can encourage the majority of websites at the center of this illicit cyberlocker eco-system to become (more) legitimate.
Cutting off the money that feeds this pirate profit pyramid is one part of the equation, but there’s also another component that may be equally important. It’s a solution that it’s already working right in our own back yard.
I look to Youtube’s solution to piracy as an imperfect, but reasonable fix. Let’s meet the pirates halfway. Why not ask them to set up Content Management Systems (CMS) like the one Youtube has? A system like this would allow content owners to determine the fate of their work. A CMS system basically allows for the fingerprinting of content so that infringing content can be instantly identified upon upload to the cyber locker site.

Dashboard for Youtube’s “Content Management System.”
The content owner could then determine, as they do on Youtube, whether to remove the content, monetize the content, or block it in certain territories. In this scenario the cyberlocker can still earn money off uploaded content, but only at the discretion of the content owner. Users will also be less inclined to post infringing content in the first place. It’s a solution that allows the content owner to take back control from the pirates (thieves) and earn income off files that previously were simply stolen. In this equation, at least everyone gets a piece of the pie.
It’s at this point that the false “piracy is good for business” refrain parroted by piracy apologists begins to gain some traction and some truth. If piracy’s black market business model can be remolded into a practice that can financially compensate the content creator–and restore their control of the content–perhaps it could become better for business.
The problem is that cyberlockers are not going to adopt a CMS system just to be nice. Youtube, a U.S. company, was forced to act under threat of ongoing litigation and legislation. The only way today’s crop of cyberlockers can be forced to institute similar content ID systems is if their current business model becomes unsustainable. For that to happen, like Youtube, they too will need to face the threat of litigation and/or the long arm of the law. At this point, that puts the ball squarely back in the lap of Congress.
That is what I know…
To be continued:
Part Two- The Dysfunctional DMCA (coming soon)
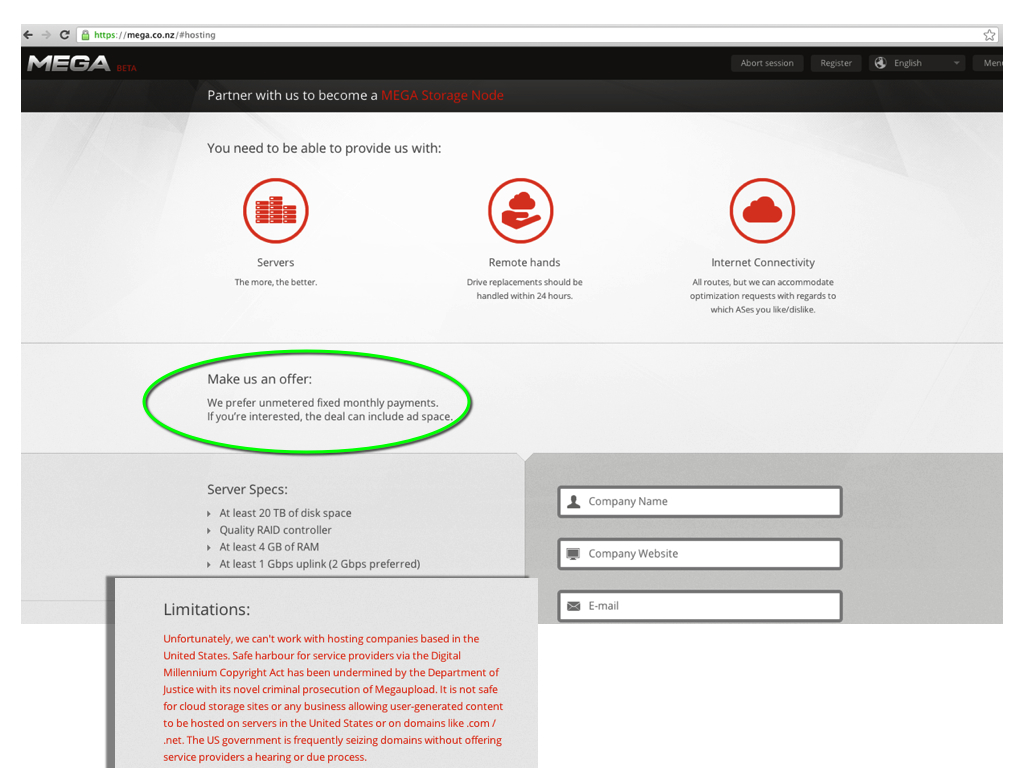
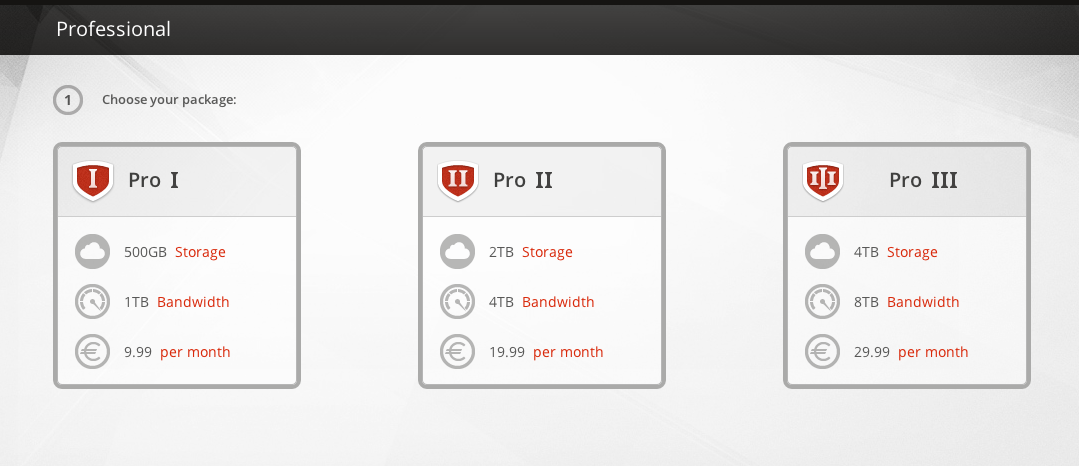
 Kim Dotcom’s much ballyhooed new venture, Mega, has gone live. and is, according to a tweet from the mastermind himself, already wildly popular, “250,000 user registrations. Server capacity on maximum load. Should get better when initial frenzy is over. Wow!!!” It’s no great surprise that there’s a lot of early interest in site, but the real question going forward is whether anti-piracy activists should be running scared? For now, it seems too early to tell. The key to whether this new cloud-based file-sharing site will become the new nexus for online piracy depends on what business model is used, and at this point, it’s difficult to decipher exactly how this will all play out.
Kim Dotcom’s much ballyhooed new venture, Mega, has gone live. and is, according to a tweet from the mastermind himself, already wildly popular, “250,000 user registrations. Server capacity on maximum load. Should get better when initial frenzy is over. Wow!!!” It’s no great surprise that there’s a lot of early interest in site, but the real question going forward is whether anti-piracy activists should be running scared? For now, it seems too early to tell. The key to whether this new cloud-based file-sharing site will become the new nexus for online piracy depends on what business model is used, and at this point, it’s difficult to decipher exactly how this will all play out.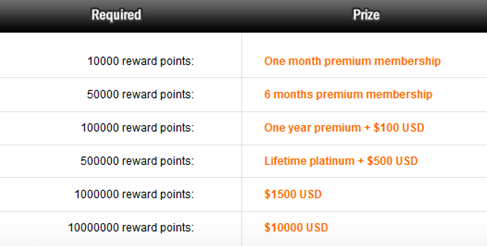 There are already various cloud-based file-sharing sites, similar to the “new” Mega–sites DropBox and YouSendIt that already allow users to easily share large files across the web. However, unlike Kim Dotcom’s now-defunct Megaupload site, these services do not incentivize uploads. In other words, in contrast to cyberlocker favored by pirates, these legit sites don’t offer cash rewards based on the number of times a file is downloaded. As a result, most people who use these cloud-based file-sharing services do so because they have actual business to conduct, or seek to share files with family or friends.
There are already various cloud-based file-sharing sites, similar to the “new” Mega–sites DropBox and YouSendIt that already allow users to easily share large files across the web. However, unlike Kim Dotcom’s now-defunct Megaupload site, these services do not incentivize uploads. In other words, in contrast to cyberlocker favored by pirates, these legit sites don’t offer cash rewards based on the number of times a file is downloaded. As a result, most people who use these cloud-based file-sharing services do so because they have actual business to conduct, or seek to share files with family or friends.